How Does the Amniotic Cavity Form
At the beginning of the second week a cavity appears within the inner cell mass and when it enlarges it becomes the Amniotic cavity. In humans it forms the innermost fetal membrane produces amniotic fluid expanding to eventually fuse with the chorionic membrane during week 8 of development.
Amnion Umbilical Cord General Embryology
Extra-embryonic mesoderm cells migrate between the cytotrophoblast and yolk sac and amnion.

. Alongside this lung secretions from the. As the amniotic fold rises and fuses over the dorsal aspect of the embryo the amniotic cavity is formed. Kavĭ-te 1.
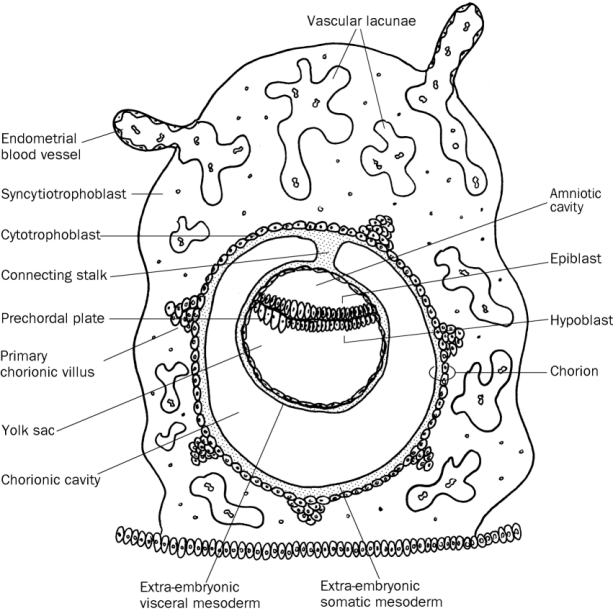
Develops into amnion blastocoel. The chorion is a double-layered membrane formed by the trophoblast and the extra-embryonic mesoderm which eventually will give rise to the fetal part of the placenta. Epiblast migrates between the epiblastic disc and trophoblast.
Cavities in the body. The amniotic cavity is formed by the fusion of the parts of the amniotic fold which first makes its appearance at the cephalic extremity and subsequently at the caudal end and sides of the embryo. The lesion produced by dental caries.
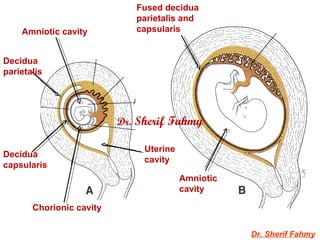
The amniotic cavity is formed by the fusion of the parts of the amniotic fold which first makes its appearance at the cephalic extremity and subsequently at the caudal end and sides of the embryo. Formation of The Amniotic Cavity. As the fetus grows the amniotic cavity expands eventually resulting in the displacement of the chorionic cavity and the uterine cavity.
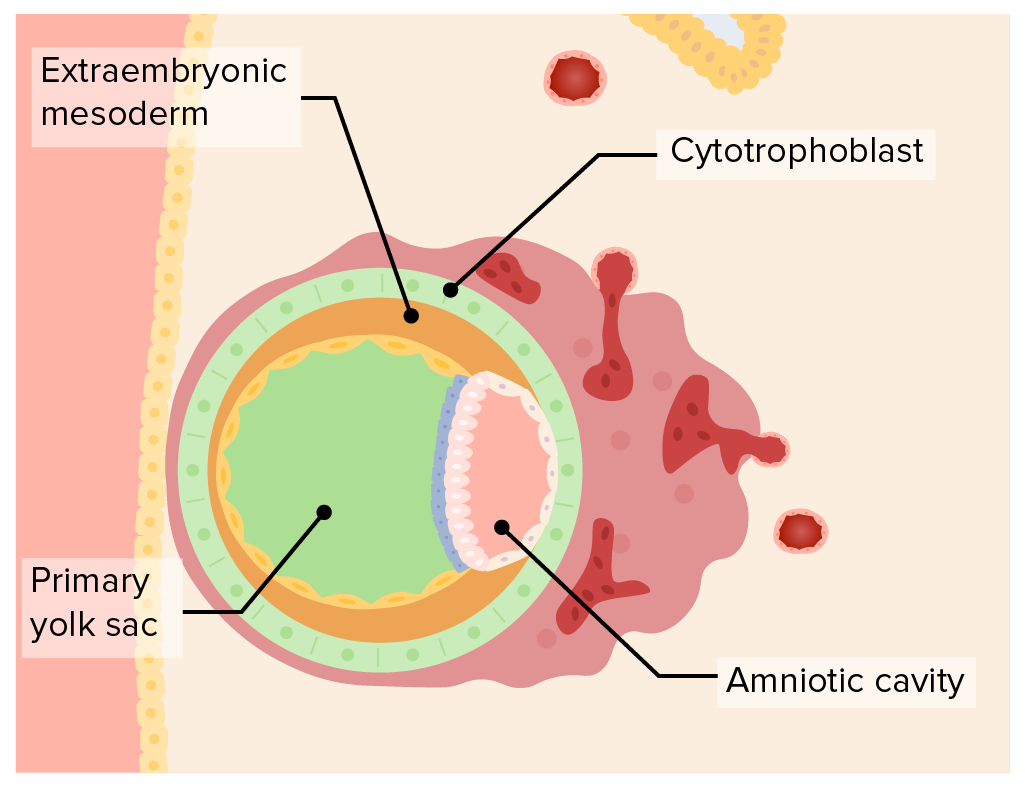
In early gestation two fluid-filled sacs surround the embryo. The ground of the amniotic cavity is formed by Epiblast. The exocoelomic membrane is derived from the hypoblast and lines the cavity that appears beneath the endoderm the primary yolk sac.
Eventually as the embryo grows and. The team tested different methods to produce amnion. The amniotic sac enlarges rapidly due to an increase in the volume of amniotic fluid.
It is aggressive and eats away at the uterine wall allowing the. Lacunae develop in the mesoderm until they coalesce into a large chorionic cavity surrounding the amniotic and yolk sac cavities. Cell layer that embeds in the uterine wall.
The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the epiblast proper which later on transforms to ectoderm. A thick soft bed of gel covered with a looser gel which Gumucio compared to a bed of fully congealed Jello with a layer of partially set Jello on top. Called also caverna and cavum.
At 10 weeks the fetus produces urine which enters the amniotic sac. The amniotic sac is formed very early in pregnancy and surrounds the embryo as a protective shell. Fertilization and the first week reaches the endomer implantation the implantation of endometrial implants of embryo mammals in the blastocyst phase.
Term for the conceptus at the developmental stage that consists of about 100 cells shaped into an inner cell mass that is fated to become the embryo and an outer trophoblast that is fated to become the associated. Hypoblast cells migrate to surround the blastocyst cavity differentiate into extraembryonic mesoderm surrounding amniotic and yolk sac cavities. The fluid contained in this sac is the source of.
The amniotic cavity is the closed sac between the embryo and the amnion containing the amniotic fluid. The chorion is a double-layered membrane formed by the trophoblast and the extra-embryonic mesoderm which eventually will give rise to the fetal part of the placenta. Epiblast cells cavitate to form the amnion an extra-embryonic epithelial membrane covering the embryo and amniotic cavity.
The amniotic sac enlarges rapidly due to an increase in the volume of amniotic fluid. In the second and third trimesters the amniotic sac expands and amniotic fluid is mainly composed of fetal urine. A hollow or space or a potential space within the body or one of its organs.
Cells from the epiblast will also eventually form the body of the embryo. In the period from fertilization to eight weeks the amniotic fluid is composed mainly of water from the mother. The amniotic cavity is the closed sac between the embryo and the amnion containing the amniotic fluid.
Fluid-filled cavity of the blastocyst blastocyst. In this structure the stem cells began to turn into amnion cells organized in a shell around an empty cavity. The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the epiblast.
Eventually as the embryo grows and folds the amnion will surround the entire embryo. Lines the blastocyst cavity. The amniotic cavity is what contains the amniotic fluid and helps hold the embryo and protect it.
The formation of the coelomic cavity begins during the fourth week of gestation when the exocoelomic cavity splits the extraembryonic mesoderm into the splanchnic mesoderm lining and the somatic mesoderm. Some epiblast cells become specialized as amnioblasts and they secrete the amniotic fluid. It develops from a combination of maternal and fetal cells that combine to form the layers of the membranes that make up its exterior.
Abdominal cavity the cavity of the body between the diaphragm above and the pelvis below containing the abdominal. 2 nd week of development through migration of epiblast cells. The fluid-filled amniotic fluid extraembryonic coelom cavity formed initially by epiblast and then lined by ectoderm and surrounding extraembryonic mesoderm.
Within the epiblast a cavity develops the amniotic cavity which fills with amniotic fluid. As the amniotic fold rises and fuses over the dorsal aspect of the embryo the. The exocoelomic cavity and the amniotic cavity.
In this way the epiblastic cells migrate between the embryoblast and trophoblast. Cavity that opens up between the inner cell mass and the trophoblast. The amniotic cavity is formed by the fusion of the parts of the amniotic fold which first makes its appearance at the cephalic extremity and subsequently at the caudal end and sides of the embryo.
Baby in Amniotic Sac at Birth.

Amniotic Egg 4 Extra Membranes Amnion Yolk Sac Chorion Allantois Amniotic Cavity Shell Albumin Female Reproductive System Anatomy Basic Algebra Cavities
Embryoblast And Trophoblast Development Concise Medical Knowledge
Comments
Post a Comment